An industrial plug is a heavy-duty electrical connector used to provide power to machines and equipment in demanding environments such as factories, construction sites, and commercial facilities. These plugs are designed to carry higher currents and voltages than standard household plugs, making them essential for powering industrial tools and systems safely and efficiently.

High Current & Voltage Capacity:
Industrial plugs are typically rated from 16A up to 125A and can support voltages ranging from 110V to 690V, depending on application needs.
Durability:
Made from heat-resistant and impact-resistant materials, industrial plugs are built to withstand harsh conditions including dust, moisture, vibrations, and extreme temperatures.
Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings:
Most industrial plugs come with IP44, IP67, or higher ratings, meaning they are resistant to water and dust—ideal for outdoor or wet environments.
Multiple Pin Configurations:
Available in 2-pin, 3-pin, 4-pin, and 5-pin versions to accommodate single-phase and three-phase power systems, including neutral and ground wiring.
Safety Standards:
Industrial plugs often meet international standards such as IEC 60309 (also known as CEE plugs), ensuring safety and compatibility across global applications.
Why Are Industrial Plugs Important?
Safety and reliability are critical in industrial operations. Industrial plugs reduce the risk of electrical hazards like short circuits or overheating by providing a secure and stable connection. Their design minimizes accidental disconnections, ensures consistent power flow, and allows for quick and easy connection/disconnection during maintenance or equipment changeovers.
An industrial plug operates as a safe and efficient connector that supplies electrical power from a source to a device or machine. While the concept is similar to a regular household plug, industrial plugs are engineered to handle higher loads, harsher environments, and more complex power requirements. Understanding how they work helps ensure proper installation, safe usage, and optimal performance in industrial applications.
Basic Working Principle
At its core, an industrial plug functions by creating a secure electrical connection between a power source (such as a distribution board or generator) and an electrical device. When inserted into a matching industrial socket or receptacle, the metal contact pins inside the plug align with corresponding terminals to complete the electrical circuit.
Key Components and Functions
Conductive Pins (Contacts)
These metal prongs transmit electrical current. They are typically made from copper or brass for high conductivity and are often plated to resist corrosion.
Insulated Housing
The outer casing of the plug is made from high-impact, flame-retardant, and weather-resistant materials. It insulates and protects the user from electric shock and the internal components from external damage.
Locking Mechanism
Many industrial plugs feature a locking ring or twist-lock system that secures the plug in place once it’s inserted. This prevents accidental disconnection during operation.
Earth (Ground) Pin
A longer or thicker ground pin ensures the circuit is grounded before live power is connected, enhancing user safety. Grounding prevents electrical shock in case of a fault.
Color Coding and Keying
Industrial plugs are color-coded and keyed to prevent mismatches in voltage and frequency. This design ensures only compatible plugs and sockets can connect.
Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
Plugs may feature waterproof or dustproof seals, ensuring functionality in wet, dusty, or outdoor environments. For instance, an IP67-rated plug is completely dust-tight and can withstand temporary immersion in water.
Electrical Connection Process
Insertion: The plug is inserted into the corresponding socket, aligning the pins and ensuring a snug fit.
Engagement: The locking mechanism (if available) is engaged to prevent accidental removal.
Current Flow: Electricity flows from the power source through the plug's pins into the connected device.
Disconnection: When the task is complete, the locking mechanism is released, and the plug is safely removed.
Application Safety
Industrial plugs are built with safety in mind. Key features like protective housings, grounding pins, and standardized pin configurations prevent electrical hazards such as arcing, overloading, or reverse polarity. Proper installation and use of the right plug type for your voltage and current rating are essential for safe operation.
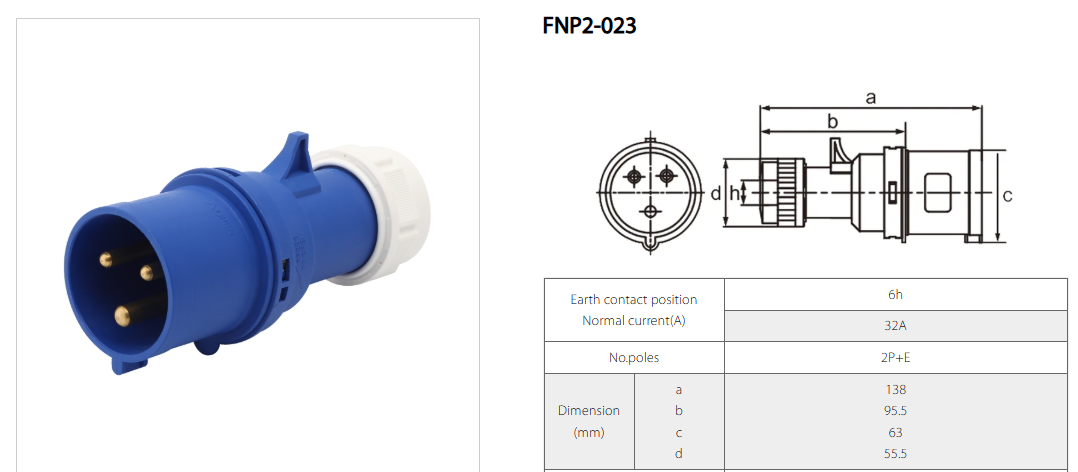
Industrial plugs come in a variety of designs and specifications, each tailored to meet specific power requirements, environmental conditions, and safety standards. Understanding the different types of industrial plugs and their applications is crucial for selecting the right one for a particular task, ensuring both efficiency and safety.
1. Standard Industrial Plugs
These are the most common type of industrial plugs, designed to work with standard electrical systems found in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and commercial facilities. They come in various voltage and current ratings to accommodate different power needs.
Applications:
Manufacturing facilities: Powering heavy machinery and equipment.
Construction sites: Connecting power tools, lights, and other construction equipment.
Warehouses: Providing power for material handling systems.
2. Weatherproof Industrial Plugs
Designed for use in harsh outdoor environments, weatherproof industrial plugs feature enhanced sealing and high ingress protection (IP) ratings, such as IP65, IP67, or higher. These plugs prevent the ingress of water, dust, and debris, ensuring reliable operation in extreme weather conditions.
Applications:
Outdoor construction sites: Powering equipment exposed to rain or dust.
Agriculture: Running irrigation systems and outdoor machinery in rainy or dusty conditions.
Mining operations: Providing power in environments with moisture and dirt.
3. High-Voltage Industrial Plugs
These plugs are specifically engineered for higher voltage systems, typically used in industrial applications requiring electricity above 1000V. They are constructed with robust insulation and safety mechanisms to prevent electrical accidents when dealing with high-voltage equipment.
Applications:
Heavy manufacturing: Powering large industrial machines like motors, furnaces, and presses.
Electrical substations: Providing power for high-voltage distribution systems.
Mining and energy generation: Running large power equipment and generators.
4. Rotary and Twist-Lock Plugs
Rotary or twist-lock industrial plugs have a unique locking mechanism that ensures the plug remains securely connected to its socket. This feature is particularly useful in environments where vibration or movement could otherwise dislodge the connection.
Applications:
Construction sites: Powering tools and equipment that experience vibrations.
Marine applications: Ensuring a stable connection in environments where the plug might be exposed to movement or water.
Portable generators: Ensuring the plug stays in place while the generator is in operation.
5. Explosive-Proof Industrial Plugs
These plugs are designed for environments with a risk of explosive gases or dust. They are built to meet specific explosion-proof standards, preventing sparks or heat from escaping the plug and causing an ignition. These plugs typically have special coatings and designs that contain any possible sparks within the plug body.
Applications:
Petrochemical industries: Powering equipment in refineries, where there may be flammable gases.
Mining operations: Protecting workers from explosive dust or methane.
Pharmaceutical plants: Preventing ignition in environments with flammable materials.
6. Heavy-Duty Industrial Plugs
Heavy-duty industrial plugs are designed for large-scale operations that require higher power delivery. These plugs are built with extra durability and can handle larger currents and mechanical stress. They often come with reinforced casings and thicker, larger pins to accommodate the increased power.
Applications:
Industrial factories: Powering heavy equipment such as presses, grinders, and large motors.
Steel manufacturing plants: Connecting large equipment used in forging and forming metals.
Transport and logistics: Powering material handling systems such as conveyors, cranes, and lifting equipment.
7. Low-Voltage Industrial Plugs
Low-voltage industrial plugs are ideal for smaller equipment, typically below 1000V. They are commonly used for indoor applications where only lower power output is required. These plugs are compact, lightweight, and easy to install, making them suitable for less demanding tasks.
Applications:
Laboratories: Powering smaller equipment and testing devices.
Small workshops: Running basic tools, lighting, and equipment.
Retail: Connecting point-of-sale (POS) systems, displays, and smaller electronic devices.
8. Pneumatic Industrial Plugs
Pneumatic industrial plugs are used to connect pneumatic systems to power sources. They are designed to handle air pressure instead of electrical currents, and they often feature quick-connect mechanisms to make installation and removal faster and more efficient.
Applications:
Construction: Powering pneumatic drills, hammers, and other air-powered tools.
Automotive industry: Running pneumatic tools and machinery for assembly lines.
Manufacturing: Connecting air compressors and pneumatic-driven conveyors or machinery.
Industrial plugs are essential components in the world of power distribution, especially in environments where durability, safety, and high performance are required. Unlike standard household plugs, industrial plugs are engineered to handle higher currents, resist harsh conditions, and ensure safe connections in demanding workplaces.
1. Powering Heavy Machinery
One of the primary uses of industrial plugs is to provide reliable power to heavy-duty machinery. These include equipment used in manufacturing, fabrication, construction, and mining. Industrial plugs ensure stable power delivery even under continuous load and mechanical stress.
Examples of machinery powered:
CNC machines
Hydraulic presses
Conveyor systems
Welding machines
2. Temporary Power Installations
Industrial plugs are widely used in temporary power setups such as outdoor events, construction sites, and emergency facilities. Their ease of connection and disconnection makes them ideal for scenarios that require rapid deployment or relocation of power sources.
Common applications:
Concerts and festivals
Outdoor markets
Emergency shelters
Temporary work camps
3. Outdoor and Harsh Environment Use
Thanks to their rugged design and weather-resistant features, industrial plugs are frequently used in outdoor environments exposed to dust, water, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. High IP-rated plugs (e.g., IP65, IP67) are specifically suited for such situations.
Used in:
Agricultural irrigation systems
Oil and gas fields
Shipyards and docks
Outdoor manufacturing areas
4. Safe Electrical Connections in Hazardous Areas
In facilities that handle flammable gases, liquids, or dust, industrial plugs rated as explosion-proof are used to ensure no ignition occurs from electrical sparks or overheating. These plugs are critical for safety compliance in such high-risk zones.
Industries that benefit:
Chemical plantsPaint factories
Grain storage silos
Petrochemical refineries
5. Distribution of Three-Phase Power
Many industrial machines operate on three-phase electrical systems, which are more efficient for high-power applications. Industrial plugs are available in multiple pin configurations to handle such power setups safely and effectively.
Three-phase power commonly supports:
Motors and pumps
Air compressors
Large HVAC systems
Industrial refrigeration units
6. Powering Mobile Equipment and Tools
In workshops, service centers, and large facilities, mobile tools or workstations often need to be moved and reconnected to power sources. Industrial plugs allow for this flexibility without compromising safety or power stability.
Mobile equipment examples:
Portable generators
Industrial vacuum units
Mobile workbenches with integrated tools
7. Electrical Testing and Maintenance
During testing, diagnostics, or scheduled maintenance, technicians use industrial plugs to safely connect or disconnect circuits. This modularity reduces downtime and ensures that power systems can be inspected or repaired with minimal disruption.
Typical tasks include:
Equipment inspection
Load testing
Preventive maintenance
Safety audits
Industrial plugs are designed for more than just transmitting power—they're built to withstand demanding conditions that traditional plugs cannot handle. In harsh environments such as factories, shipyards, mining sites, or outdoor facilities, the right electrical connection plays a crucial role in safety, efficiency, and durability.
Why Use Industrial Plugs in Tough Conditions?
When equipment is exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, dust, chemicals, or mechanical vibration, conventional power connectors can quickly degrade or fail. Industrial plugs, on the other hand, are specifically engineered to overcome these challenges, offering significant operational advantages.
Key Benefits of Industrial Plugs in Harsh Environments:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Industrial plugs often feature IP44–IP67 ratings, protecting against rain, dust, and temporary water immersion. |
| Durability | Built with high-impact thermoplastic or rubber housings, they resist breakage and surface damage. |
| Temperature Tolerance | Suitable for both high and sub-zero environments, ensuring consistent performance in any climate. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Many plugs include stainless steel parts or anti-corrosive coatings, ideal for coastal, chemical, or industrial zones. |
| Secure Locking Mechanisms | Twist-lock or screw-type connectors ensure stable contact even with vibration or movement. |
| Safety Compliance | Designed to meet strict electrical standards, minimizing arc risks, overheating, and electrical faults. |
| Easy Maintenance & Replacement | Modular designs allow for quick servicing without full system shutdowns. |
Industry Use Cases
Oil & Gas Sites: With frequent exposure to moisture, chemicals, and explosive materials, using explosion-proof and corrosion-resistant plugs is essential.
Mining Operations: Require plugs that can handle abrasive dust, vibrations, and heavy-duty equipment.
Outdoor Construction: Demands connectors that can function through rain, mud, and freezing temperatures.
Food & Beverage Processing: Needs watertight, hygienic connectors that can handle frequent washdowns.
Maritime & Shipyards: Must resist salt spray, humidity, and mechanical shock.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Though industrial plugs may have a higher upfront cost, their resistance to environmental stress means:
Fewer replacements
Less equipment downtime
Lower risk of electrical hazards
Reduced maintenance costs
In industrial electrical systems, plugs and sockets are essential for delivering reliable and secure connections between power sources and equipment. While the two are often mentioned together, their roles, construction, and applications are distinct. Understanding the difference between an industrial plug and an industrial socket is crucial for safe and efficient system design and operation.
Definition and Basic Function
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Industrial Plug | A device that connects equipment to the power source. It has male pins that fit into a socket and is typically attached to a cable. |
| Industrial Socket | A stationary device (female) mounted to a wall, panel, or machine that receives the plug. It connects the incoming power to the plugged-in equipment. |
Key Differences
| Feature | Industrial Plug | Industrial Socket |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Transfers power from a socket to a device | Receives the plug to deliver power from the source |
| Location | Usually connected to mobile equipment or tools | Fixed to a wall, distribution board, or equipment panel |
| Design | Includes protruding male pins | Includes recessed female contacts |
| Installation | Cable-mounted | Surface- or flush-mounted |
| Portability | Mobile, easily detachable | Stationary, not typically moved |
| Safety Features | May include strain relief and cable grips | Often includes shutters, interlocks, or IP-rated covers |
| Usage Example | Plug on the end of an extension cord or industrial machine cable | Socket on a power panel or machinery wall |
Safety and Compatibility
Industrial plugs and sockets must be matched in:
Voltage and Current Ratings (e.g., 230V/16A or 400V/32A)
Number of Poles (2P+E, 3P+N+E, etc.)
Pin Configuration (to prevent incorrect mating)
Protection Ratings (e.g., IP44 for splash protection, IP67 for waterproofing)
Using mismatched or incompatible components can result in overheating, arcing, or connection failure.
Applications
Industrial Plug: Used on machinery, tools, portable equipment, or extension cables.
Industrial Socket: Installed in workshops, factories, construction sites, and any fixed power source point.
Electrical plugs may seem similar at a glance, but their construction, purpose, and technical specifications vary significantly depending on the environment they are used in. Two common types are industrial plugs and domestic plugs. Understanding the differences between them is essential for ensuring safety, compatibility, and efficient power distribution.
| Feature | Industrial Plug | Domestic Plug |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Used in factories, workshops, construction sites, etc. | Used in homes and standard consumer appliances |
| Voltage & Current | High (e.g., 230V/400V, 16A–125A or more) | Lower (typically 110V–240V, 5A–15A) |
| Durability | Built for rugged use, resistant to water, dust, impact | Basic plastic build, suitable for indoor, light-duty use |
| Design | Larger, heavier, with protective casings | Compact, lightweight |
| Pin Configuration | Multiple pins (2P+E, 3P+N+E), locking mechanisms | Usually 2 or 3 flat or round pins |
| Standards Compliance | IP-rated (e.g., IP44, IP67), industrial safety standards | Domestic safety standards |
| Usage Flexibility | Supports 3-phase or single-phase high-power equipment | Only supports standard single-phase devices |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to materials and features | More economical and widely available |
Industrial Plug Overview
Industrial plugs are designed for high-power equipment in challenging environments. They often have watertight or dustproof protection, robust housings, and secure locking systems. They are critical in settings where equipment must run safely under harsh or outdoor conditions, such as in manufacturing plants, construction zones, or shipyards.
Typical uses include:
Welding machines
Industrial ovens
Power distribution boards
Portable generators
Domestic Plug Overview
Domestic plugs are found in everyday environments, including households, offices, and light commercial areas. They connect common devices like TVs, microwaves, or lamps to wall sockets. Their construction focuses more on convenience and size rather than extreme durability.
Common characteristics:
Simple design with minimal protection
Usually rated for lower amperage
Easily replaceable or interchangeable
Choosing the right industrial plug for your equipment is crucial to ensure efficiency, safety, and longevity in operation. Industrial plugs are designed for demanding environments, and selecting the right one depends on several factors including the type of equipment, power requirements, and environmental conditions. In this guide, we will break down the key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
1. Understand the Power Requirements
Before selecting an industrial plug, you need to understand the power requirements of the equipment you're using. Industrial plugs are rated for different voltage levels and current capacities.
Voltage Rating: Common industrial plug voltage ratings include 110V, 220V, 380V, and 480V. Ensure that the plug matches the voltage required by your equipment to avoid underperformance or even equipment damage.
Current Rating: The current rating of the plug must align with the power requirements of your equipment. Industrial plugs can handle currents ranging from 16A to more than 100A. Choose a plug that supports the specific current needed by your machinery or tools.
Tip: Always verify the voltage and amperage on the equipment's specifications and match it with the plug's rating.
2. Choose the Right Type of Connection
Industrial plugs come in different configurations depending on the type of equipment and the phase of power supply. You’ll typically find the following types:
Single-phase Plugs: For light to medium-duty equipment, single-phase plugs are sufficient. These are commonly used for smaller machinery, tools, and appliances.
Three-phase Plugs: For heavy-duty or large-scale industrial machinery, a three-phase plug is often required. These plugs distribute power more efficiently and are used for large motors, compressors, and high-power equipment.
Tip: If you're working with high-power equipment, make sure the plug and socket support a three-phase connection to distribute the load efficiently.
3. Consider the Environmental Conditions
Industrial environments can vary greatly, and the plug you choose needs to withstand the conditions of the environment it will be used in. Consider the following factors:
Waterproof and Dustproof: If the plug is to be used outdoors or in harsh environments (e.g., construction sites, factories), look for plugs with an IP rating (Ingress Protection) such as IP44, IP67, or IP69. These ratings ensure the plug is resistant to dust, water, and other contaminants.
Corrosive Environments: For environments with high humidity, chemicals, or saltwater exposure (e.g., marine environments), choose plugs with corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or specialized plastic housing.
Tip: Check the IP rating of the plug to ensure it is suitable for the environmental conditions where it will be used.
4. Select the Right Size and Fit
Industrial plugs come in various sizes, and it's essential to select the right one to fit the socket and your equipment. This ensures a secure connection that won’t cause power loss or create a fire hazard.
Pin Configuration: Different plugs have different numbers of pins (e.g., 2-pin, 3-pin, 4-pin, etc.), and each configuration serves a specific purpose. Ensure that the number of pins in the plug matches the socket and equipment requirements.
Locking Mechanisms: Some plugs come with locking mechanisms to ensure a secure connection that won’t loosen during operation. This is particularly important in environments with high vibration or movement.
Tip: Ensure the plug and socket match in terms of pin configuration and locking mechanisms.
5. Durability and Material
Industrial plugs need to be tough and durable. The material used in their construction plays a key role in how long they will last and how well they perform under extreme conditions.
Housing Material: Choose plugs made from materials like reinforced plastic, rubber, or metal alloys for durability and impact resistance.
Contact Material: The plug's contacts should be made of high-quality materials such as brass or copper for better conductivity and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Tip: Look for plugs made from heavy-duty, corrosion-resistant materials to ensure they last in tough industrial settings.
6. Safety Features
Safety should always be a priority when selecting industrial plugs. Many modern plugs come with built-in safety features, such as:
Safety Shutters: These prevent accidental contact with live terminals and are especially important in high-traffic areas.
Overload Protection: Some industrial plugs are designed with built-in overload protection to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires.
Tip: Always choose plugs that meet the relevant safety standards for your industry.
7. Compliance with Industry Standards
Finally, ensure that the plug complies with industry standards and regulations. Look for certification marks such as CE, UL, or IEC that indicate the plug has been tested for safety and performance.
Installing an industrial plug correctly is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of equipment and preventing electrical hazards. Proper installation not only ensures that the plug functions efficiently but also helps to protect users from electrical shocks and fires. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to install an industrial plug safely.
1. Preparation Before Installation
Before you begin the installation process, it's essential to gather the necessary tools and ensure that you're working in a safe environment.
Tools Required:
Screwdriver
Wire stripper
Insulation tape
Cable cutters
Voltage tester
Safety Precautions:
Power Off: Always ensure that the power is turned off before beginning any electrical installation. This is the most important step to prevent electric shocks.
Check the Voltage: Use a voltage tester to ensure that the system is not live. This is critical when working with industrial equipment.
Select the Right Plug: Ensure the industrial plug you choose matches the equipment's voltage, current rating, and phase. Check the plug's specifications and confirm that it meets the electrical requirements of the equipment you are connecting.
2. Inspect the Cable and Plug Components
Before installing the plug, inspect the cable and components for any signs of wear, damage, or fraying. Ensure the cable's insulation is intact and there are no exposed wires that could cause a short circuit or shock.
Cable Inspection:
Verify the cable's size, insulation, and type to ensure compatibility with the plug.
Ensure the wire gauge is suitable for the power rating of the equipment.
Plug Inspection:
Make sure the industrial plug is in good condition with no visible cracks or damage.
Check that the pins inside the plug are not bent and the contacts are clean.
3. Stripping and Preparing the Wires
Once the components are checked and ready, you will need to strip the insulation from the cable to expose the copper wires. The following steps should be taken:
Strip the Wires:
Using wire strippers, remove the outer insulation to expose the internal wires.
Strip the insulation from the individual wires by about 1 to 2 inches (depending on the plug's size and requirements).
Prepare the Wires for Insertion:
Ensure the copper wire is clean and free of any fraying or corrosion.
Twist the exposed copper wire strands tightly to prevent any loose ends from causing a short circuit.
Check for Correct Polarity:
If applicable, ensure that the live (hot) wire is connected to the correct terminal in the plug. Industrial plugs typically have color-coded terminals for live, neutral, and ground wires.
4. Connecting the Wires to the Plug
Now that the wires are prepared, you can begin connecting them to the terminals inside the industrial plug.
Connect the Live (Hot) Wire:
Insert the stripped end of the live wire (typically red or black) into the terminal marked "L" (Live).
Tighten the terminal screw securely to hold the wire in place.
Connect the Neutral Wire:
Insert the stripped end of the neutral wire (usually blue or white) into the terminal marked "N" (Neutral).
Again, ensure the terminal is tightened properly to avoid any loose connections.
Connect the Ground Wire:
If the plug has a ground terminal (typically marked "G" or "E"), connect the ground wire (green or green with a yellow stripe) to this terminal.
Ensure that the ground wire is securely connected to ensure safety.
Double-Check Wire Connections:
After connecting all wires, double-check to ensure they are inserted into the correct terminals and securely tightened. Loose connections can cause electrical hazards.
5. Assembling the Plug
Once the wires are connected securely to the plug's terminals, you can proceed to assemble the plug.
Secure the Cable:
Tighten the strain relief clamp (if provided) around the cable to prevent the wires from coming loose or being damaged.
Ensure that the outer insulation of the cable is held securely by the strain relief mechanism.
Close the Plug Housing:
Carefully close the plug casing, ensuring the internal wiring is neatly placed without any exposed wires.
Tighten all screws on the plug casing to ensure a secure, tight fit.
6. Testing the Installation
Before you use the industrial plug, it's important to test the installation to ensure that the plug is functioning properly and safely.
Check for Proper Connection:
Use a multimeter or voltage tester to check the continuity of the connections.
Verify that the live, neutral, and ground wires are connected to the correct terminals.
Test the Plug Under Power:
Turn on the power and use the equipment to test the plug's functionality.
Ensure that the equipment runs smoothly without any power interruptions, overheating, or tripped breakers.
Inspect for Heating:
During the initial test, check the plug for any signs of overheating or unusual heating of the wires or plug housing.
If the plug becomes hot, immediately disconnect the power and inspect the connections for any faults.
7. Safety Check and Final Inspection
After the installation is complete and the plug is functioning correctly, perform a final safety check:
Check the Plug for Stability:
Ensure the plug is securely connected to both the socket and the equipment.
Check the insulation for any exposed or damaged areas.
Monitor the Equipment:
Regularly monitor the equipment and plug during its operation, particularly in the initial hours of use. Ensure there are no unusual noises, overheating, or signs of damage.
Industrial plugs are vital components used in many industries to ensure a stable and safe connection between electrical equipment and power sources. To ensure that these plugs operate efficiently and remain safe for use, regular maintenance is crucial. Proper maintenance helps to maximize the service life of industrial plugs, reduces the likelihood of failure, and minimizes the risk of electrical hazards.
1. Regular Inspection of Industrial Plugs
The first step in maintaining industrial plugs is to conduct frequent inspections. Regularly check the plugs for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Look for the following during your inspections:
Physical Damage: Examine the plug for any visible cracks, chips, or broken parts. Physical damage can compromise the integrity of the plug and lead to short circuits or other safety issues.
Corrosion: Check the terminals and connectors for corrosion, especially if the plugs are used in humid or outdoor environments. Corrosion can weaken the electrical connection and increase the risk of failure.
Loose Connections: Ensure that the wires are tightly secured within the terminals. Loose connections can cause overheating, power interruptions, or spark hazards.
2. Clean the Industrial Plug Regularly
Dirt, dust, and debris can accumulate inside industrial plugs, affecting their functionality and safety. Regular cleaning helps to maintain the performance of the plugs and prevents damage caused by foreign particles.
Turn Off Power: Always ensure that the power is switched off before cleaning the plug to avoid electric shock or injury.
Use a Soft Brush: Use a soft brush or cloth to remove any dirt, dust, or grime from the surface of the plug. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage the plug's materials.
Clean Terminals: If necessary, gently clean the terminals using a cloth or specialized cleaning solution designed for electrical components. This helps to prevent corrosion and ensures that the plug maintains good conductivity.
3. Lubricate the Moving Parts
Some industrial plugs feature moving components, such as locking mechanisms or hinges. It's important to lubricate these parts regularly to ensure smooth operation and to prevent wear and tear.
Use Appropriate Lubricants: Apply a light coat of lubricant to the moving parts, ensuring that the lubricant is designed for electrical components. Do not over-lubricate, as excess lubricant can attract dirt and dust.
Check for Sticking Parts: If any parts are sticking or difficult to operate, lubricating them may resolve the issue and improve the plug’s overall performance.
4. Check for Overheating or Overloading
Overheating is a common issue that can lead to plug failure. Overloading an industrial plug beyond its rated capacity can result in damaged connectors, burnt wires, and increased risks of electrical fires.
Monitor Load Levels: Ensure that the plug is always used within the specified load limits. Overloading can cause the plug to overheat and degrade its components.
Check for Heat Marks: Look for discoloration or heat marks on the plug, which could indicate overheating. If overheating is observed, disconnect the equipment immediately and inspect the plug for damage.
5. Ensure Proper Storage
When not in use, industrial plugs should be stored properly to prevent exposure to moisture, dust, and physical damage. Improper storage can shorten the lifespan of the plug and render it unsafe for use.
Store in a Dry, Clean Area: Ensure that the plugs are stored in a dry, clean location away from moisture and dirt. Humidity and dirt can cause corrosion and damage to the connectors.
Use Protective Covers: If possible, store plugs with protective covers to prevent exposure to dust or physical damage. This is especially important in environments where plugs are exposed to harsh elements.
6. Replace Damaged Plugs Immediately
If an industrial plug shows signs of irreparable damage, such as cracked housing, corroded terminals, or worn-out locking mechanisms, it is important to replace it immediately.
Avoid Temporary Fixes: Do not attempt to repair an industrial plug with temporary fixes like tape or makeshift parts. Damaged plugs should be replaced to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Use High-Quality Replacements: When replacing a damaged plug, always use a high-quality, compatible replacement that meets the specifications of the original plug.
7. Periodic Testing for Electrical Continuity
To ensure that the industrial plug is functioning correctly, periodic electrical testing is essential. This can help identify any potential issues early and prevent accidents or equipment malfunctions.
Use a Multimeter: Regularly use a multimeter to test the electrical continuity of the plug. This will help you identify any issues with the wiring or connectors that may affect the performance of the plug.
Inspect Electrical Contact Points: Check the contact points within the plug for any signs of wear or corrosion, as these can interfere with the electrical connection and cause failures.
By following these simple yet effective maintenance tips, you can maximize the service life of your industrial plugs and keep them functioning at peak performance. Regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and proper storage are essential to ensure safety and efficiency. Neglecting maintenance can lead to increased downtime, costly repairs, and potential safety hazards.
For high-quality industrial plugs and other electrical components designed for durability and reliability, Fly-Dragon Electrical Co., Ltd. offers a wide range of products tailored to meet the needs of various industries. Our expert team is dedicated to providing innovative solutions that enhance the safety and performance of your electrical systems. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services!