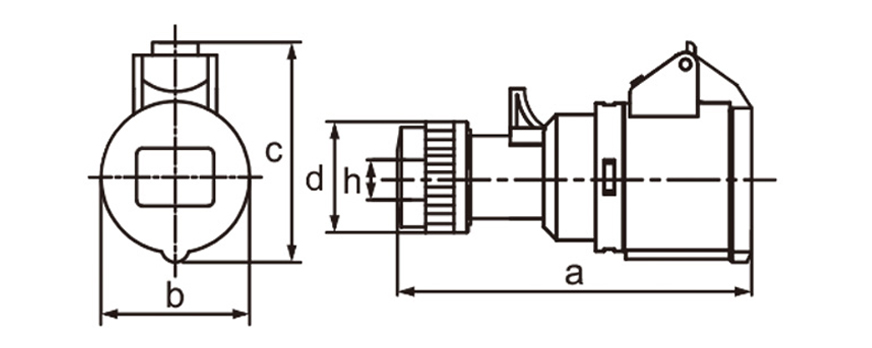
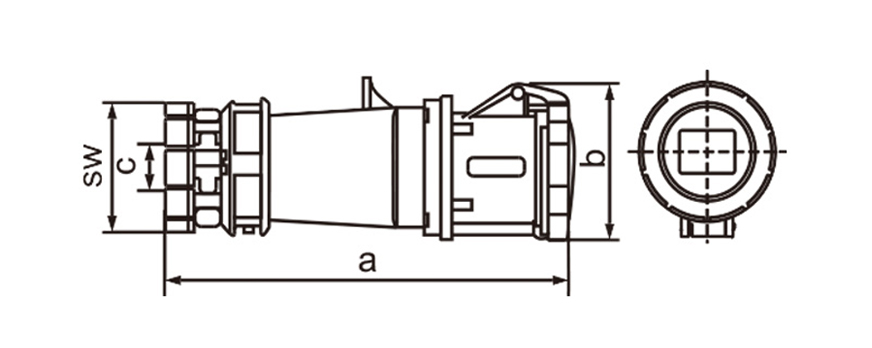
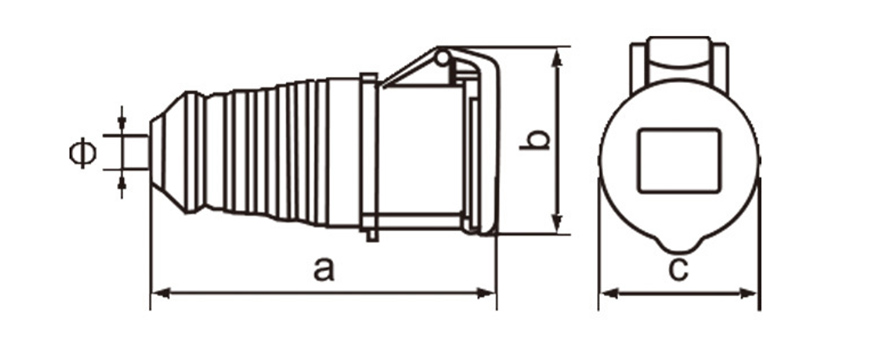
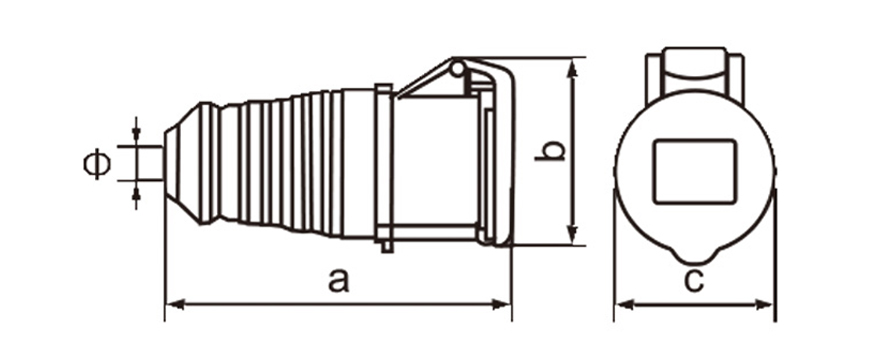
Industrial plug socket connectors are a foundational component in modern power distribution systems, especially in environments where stability, safety, and durability matter more than convenience. In manufacturing plants or logistics hubs as well as renewable energy projects and major construction sites these connectors work behind the scenes to deliver steady power to equipment even under tough conditions.
Design Characteristics and Standardization in Industrial Environments
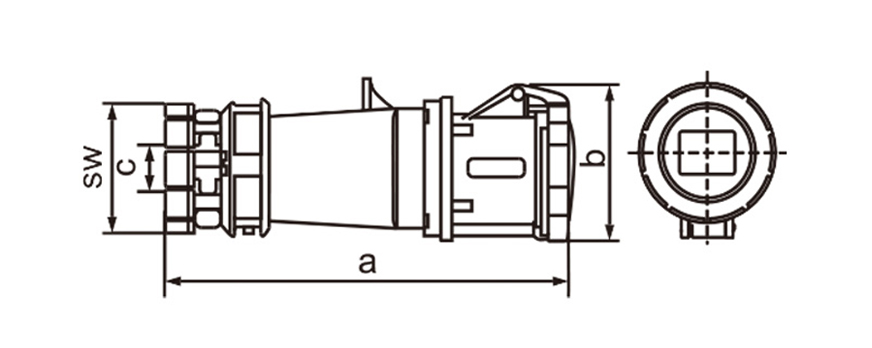
Industrial plug socket connectors differ from household plugs because they manage much higher voltages and currents in rough surroundings. Settings often involve dust or moisture along with vibration chemical splashes and wide temperature swings yet the design tackles those threats head-on. Builders rely on tough thermoplastics rubber mixes and metals that resist corrosion to make the connectors last longer with fewer breakdowns.
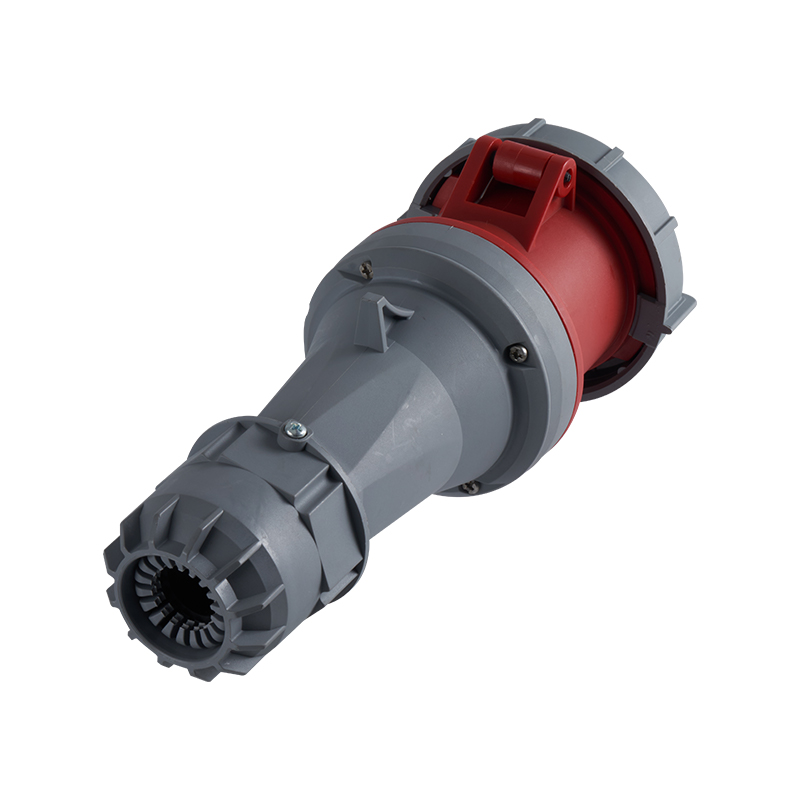
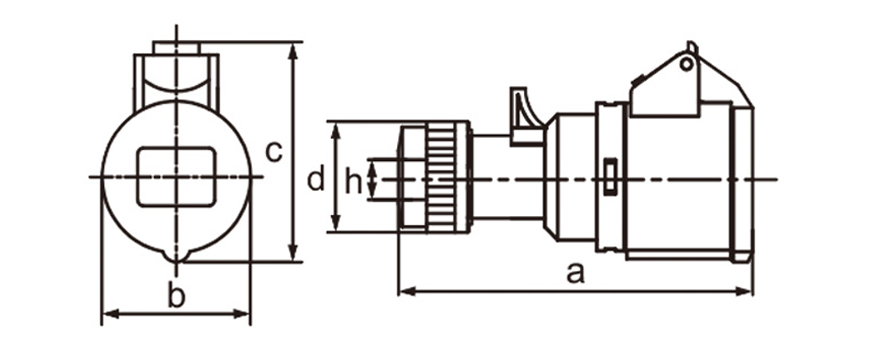
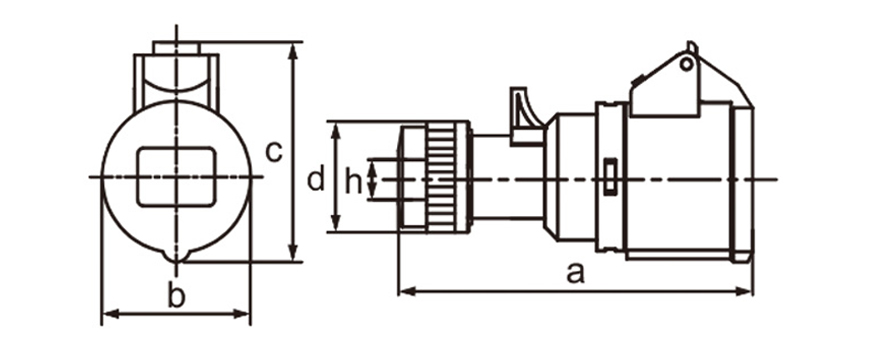
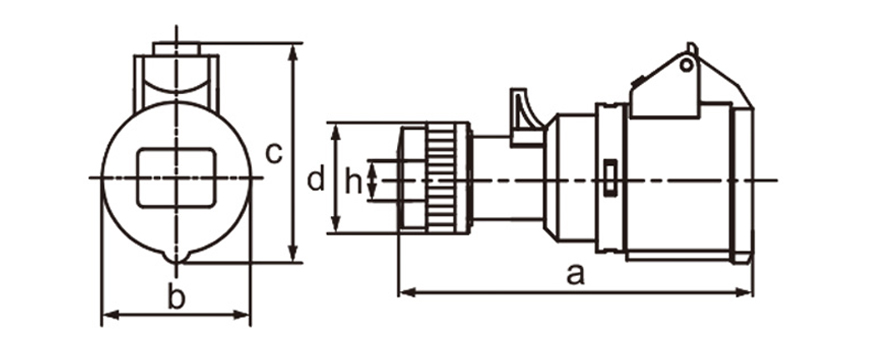
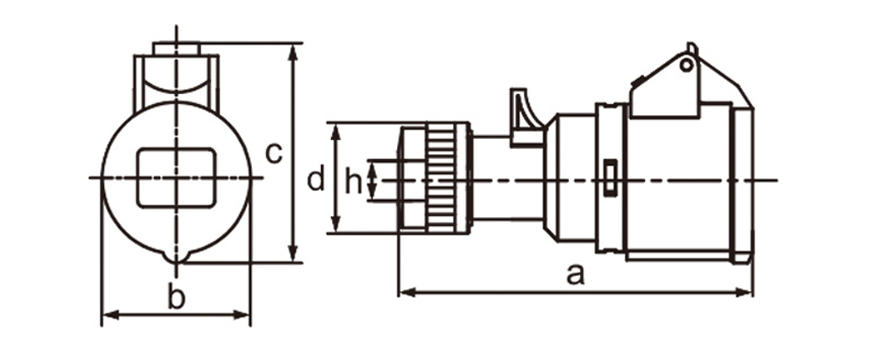
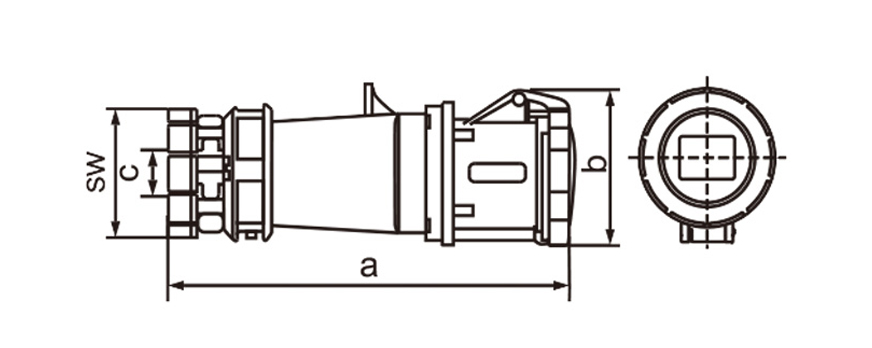
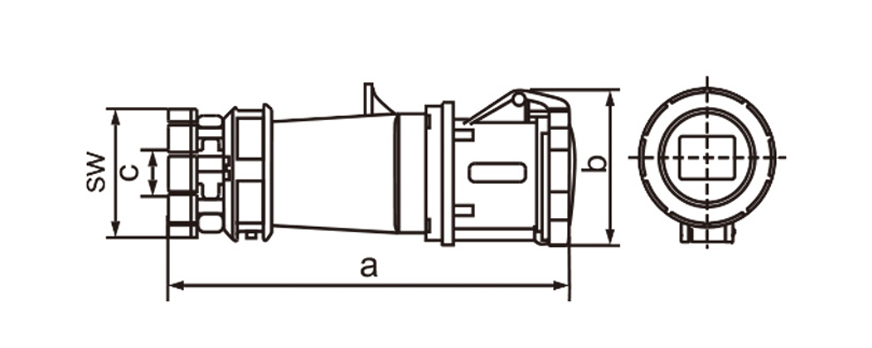
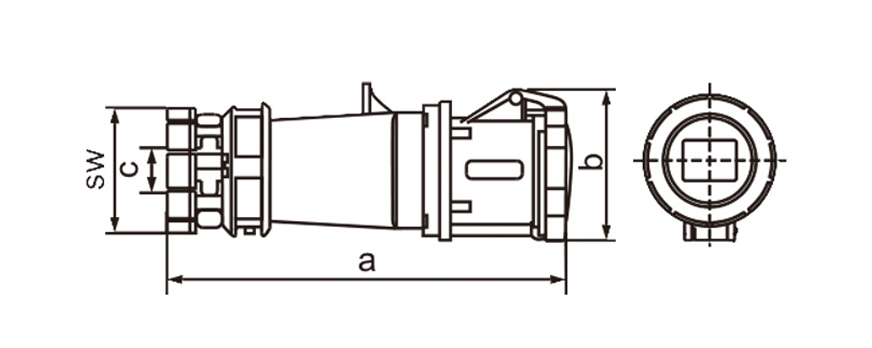
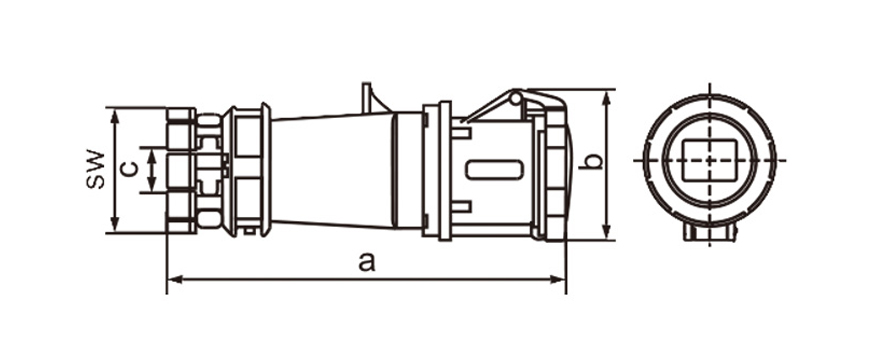
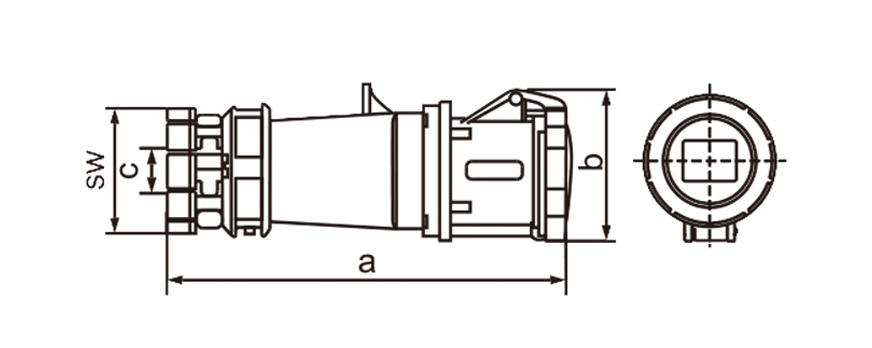
One of the most defining characteristics of industrial plug socket connectors is standardization. International standards such as IEC 60309 (also known as IEC 309 or CEE) define color coding, pin configurations, voltage ranges, and frequency ratings. This standardization minimizes the risk of incorrect connections, which can lead to equipment damage or serious safety incidents. For example, different colors are used to indicate voltage levels, making it easier for technicians to identify compatible connectors at a glance, even in complex installations.
Current and voltage ratings play a key role in choosing connectors. Industrial types often come in strengths of 16A 32A 63A or 125A and work with single-phase or three-phase power. That range suits everything from small portable tools up to massive machinery. Three-phase versions stand out in places running motors compressors and other heavy loads day in and day out.
Safety, Protection, and Mechanical Reliability
Ingress protection (IP) ratings play a central role in connector selection. An IP rating indicates resistance to dust and water, with higher numbers offering better protection. In outdoor or wash-down environments, connectors with IP67 or IP68 ratings are often preferred. These designs prevent moisture ingress even when temporarily submerged, which is critical in sectors like food processing, mining, and marine operations.
Industrial plug socket connectors incorporate safety features right into their core design. Locking mechanisms built into many models stop accidental pull-outs while equipment runs. That matters most with mobile devices or setups facing constant vibration. Certain designs ensure the ground pin connects before others and breaks contact only after everything else has disconnected which cuts down shock hazards. Contacts made to withstand heat avoid warping or breaking even during prolonged heavy loads.
Mechanical strength plays a key role too. These connectors endure countless mating cycles along with knocks and tugs from thick cables. Sturdy housings combined with built-in strain relief shield the wires inside and keep connections reliable year after year. In busy workplaces those traits cut repair needs and keep operations running longer without interruptions.
Modular Power Distribution and Evolving Industry Demands
Industrial plug socket connectors also support modular and scalable power distribution. In temporary installations, such as events, construction sites, or emergency response setups, connectors allow power systems to be deployed and reconfigured quickly. This modularity improves efficiency and reduces installation complexity, especially when compared to hardwired solutions.
With the growth of automation and smart manufacturing, connector design is evolving to meet new demands. Modern industrial environments often integrate sensors, control systems, and networked equipment alongside power delivery. While traditional industrial plug socket connectors focus on power transmission, their role within larger interconnected systems has become more strategic. Reliable power connections are essential to maintain data integrity, system uptime, and overall operational efficiency.
Sustainability has started to play a bigger role in this industry. Many manufacturers now turn to recyclable materials while aiming for products that last longer and designs that cut down on energy waste by boosting conductivity. In big operations these minor improvements at the connector stage often lead to noticeable drops in overall power use as years pass.
Choosing the proper industrial plug socket connector goes beyond any one spec. Teams weigh electrical needs against harsh surroundings along with safety rules and future upkeep demands. Engineers together with buyers tend to view these connectors less as simple parts and more as ways to shield machines workers and output from risks.
With industrial setups growing ever more varied the need for solid power links stays unchanged. These plug socket connectors draw little notice yet they hold up safe smooth and tough-running systems at the heart of today's industrial world.


 English
English Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch